You have no items in your shopping cart.
Barcode & Auto ID Solutions

Barcode scanners are currently essential in every industry, relying on technology and modern innovation.
To enhance the efficiency of service management and operations, one technology that has become crucial is Automatic Identification (Auto ID).
Barcode reader solutions and Auto ID have been invented and developed to serve as tools for identifying living beings and objects with unique characteristics. These technologies facilitate operations that require quick and accurate data recording, replacing manual counting or note-taking, and avoiding errors in related processes such as retrieval and verification. Numerous companies and retail outlets utilize this technology alongside their product manufacturing processes, inventory control, and logistics, to boost their competitive edge in the business.
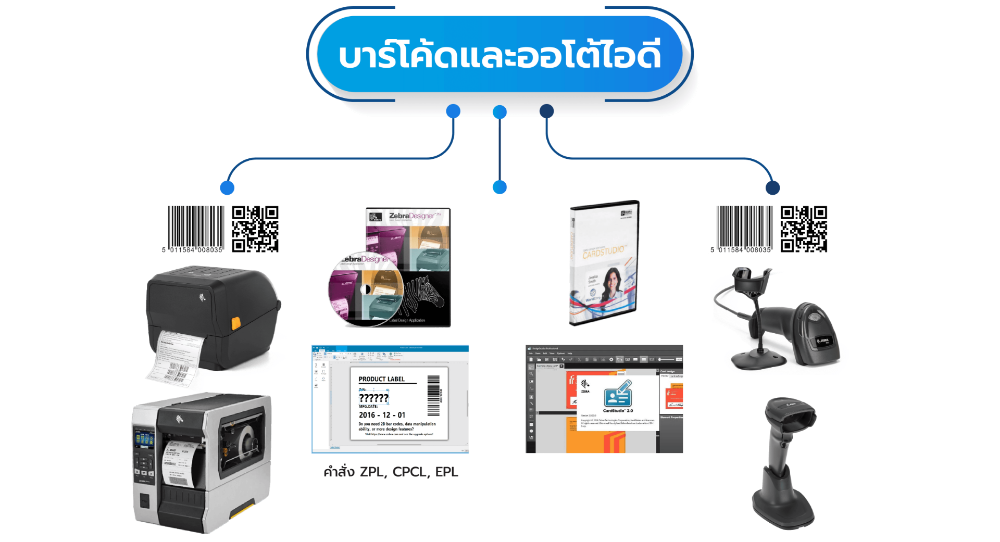
Barcodes are divided into two main types: 1D (One Dimensional) barcodes and 2D (Two Dimensional) barcodes.
| 1D barcodes, or One-Dimensional barcodes | 2D barcodes, or Two-Dimensional barcodes |
|
|
 |  |


| บาร์โค้ดสแกน ZEBRA DS1001 | บาร์โค้ดสแกน CODESOFT BC-603BT | ||
Barcode Scanners: They function similarly to a keyboard in entering data into a computer system. When a barcode scanner scans a barcode, the computer translates it into numerical or textual data, which then appears on the display screen, making it comprehensible. Barcode scanners significantly enhance work efficiency, speed, and accuracy, replacing manual data entry and reducing errors and delays.
Barcode scanners come with different types of reading heads, divided into four main categories based on the technology used:
CCD (Charge Coupled Device): This technology uses CCD sensors to capture light from barcodes. The scanner's beam is elongated, making CCD scanners suitable for general use, such as reading barcodes on product packaging.
Laser: Utilizes laser beams to read barcodes, with the scanner's beam being a straight line. Laser scanners are ideal for applications requiring high precision, such as reading barcodes on small-sized products or products with high reflectivity.
Omnidirectional: Employs a circular reading head that rotates to read barcodes from all directions. Omnidirectional scanners are convenient for reading barcodes on irregularly shaped products.
Imager: Uses digital cameras to read barcodes. Imager scanners are suitable for high-precision applications and can read various barcode formats, such as 1D, 2D, and specialized barcodes.
When purchasing a barcode scanner, consider the following to ensure it meets your operational needs:
Type of Barcode: There are several types of barcodes, such as 1D, 2D, and specialized barcodes. The choice of scanner should be based on the type of barcode to be read. For example, if you need to read 2D barcodes, a scanner using Imager technology would be a better choice.
Operating Environment: The working environment, such as lighting, temperature, and humidity, can affect the performance of barcode scanners. Choose a scanner suitable for your environment. For example, CCD technology might be a better choice in low-light conditions.
Usage: Barcode scanners come in various forms, such as handheld, desktop, or automated systems. Consider how you plan to use the scanner, such as handheld for portable use.
Budget: Barcode scanners vary in price, so select one that fits your budget.
Mobile Computers: Handheld barcode scanners designed for industrial use enhance production efficiency and customer service levels. These portable, durable computers respond to all operational demands and can read barcodes.
Stock Counting Devices: Solve inventory problems, whether large or small quantities, by scanning barcodes and inputting numbers, time, and date of scanning, or simply scanning the barcode alone. The data can be exported as a text file, which can be used with Excel or other stock counting programs immediately.
Passport Readers: Address the needs of travel and tourism services, such as airports, airlines, hotels, tours, transportation companies, and cruise ships. Passport readers can be used to check traveler information, such as name, surname, nationality, date of birth, expiration date, visa, etc., to facilitate travel and tourism processes.


 |
Request for Quotation Call 02-0263361-2 EXT 121, 124, 119
Line official ID @pospak



































